|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> from .xyz file Gridding |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> from .xyz file Gridding |
  
|
Purpose
To create a model from random or grid co-ordinate data in a .xyz file (either comma or space deliminated). This function enables the creation of a model from very large data sets with millions of points for example OS Land-Form PROFILE DTMs or OS Terrain® 5. If the .xyz data is in two or more files they can be merged together by menu item File utilities, .xyz Co-ordinate files, Merge and Extract. Typical data will look line this :-
180000,44680,82.4
180000,44690,82.9
180000,44700,83.5
180000,44710,84.1
180000,44720,84.6
In addition to the typical ZTV applications this is also suitable for working with Hydrographic survey and Lidar data. This method is different to the other model creation options by not making the triangulation directly respect the source data but works by "overlaying" a grid at a specified interval over the data and "averaging" the source data onto the grid intersections. This provides a valuable means of making a "well resolved" model comprising 45deg. right angled triangles that logically considers all source data in the file and writes a manageable size of model.
Operation
Select input .xyz file and enter the name of the output model.
The program reads all lines in the file and reports content information in this dialogue :-
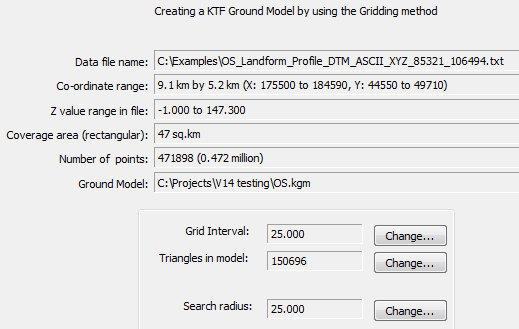
Use the Change... button to set a suitable number of triangles or control this by entering the grid interval. With over 1 million points, to get "a feel" for the number of triangles initially try around 200,000 to 250,000 for example - performance will depend on PC specification. Every point within the search radius (circle based on a grid intersection) is added to a weighted average for that grid intersection. The further away a point is from the intersection the less its weight. E.g. if a point is at the intersection the weight will be 100%, if 15% of the search radius away it's weight will be 50% and if 60% of the search radius away the weight will only be 2.5%. In a word the weight drops logarithmically related to the distance from the grid intersection.
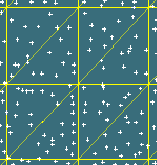
Example random data used to calculate levels at triangle corners
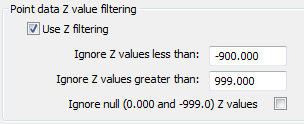
The data points can also be filtered by the Z value. Useful option if the data set to make the ground model from marks areas with no level value as "-999.0" for example.